
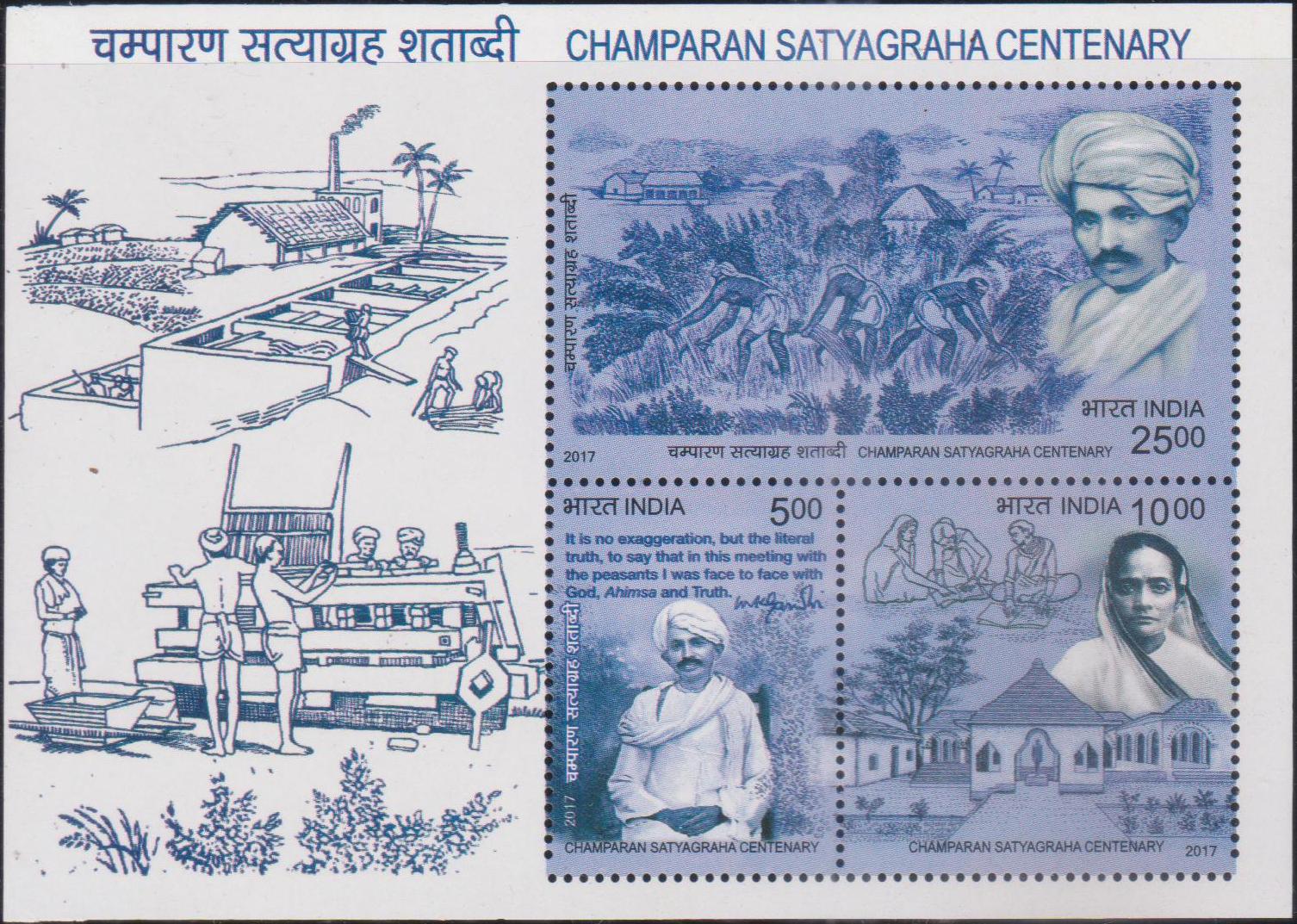
India on 1942 Freedom Movement
A Miniature Sheet consisting of 8 nos. of commemorative postage stamp on the 75th anniversary of the Quit India movement (August Movement) :








 Issued by India
Issued by India
Issued on Aug 9, 2017
Issued for : The Department of Posts is pleased to issue a set of eight Commemorative Postage Stamps on the completion of 75 years of 1942 Freedom Movement.
Credits :
Stamp/Miniature Sheet/FDC/Brochure : Sh. Sankha Samanta
Cancellation Cachet : Smt. Alka Sharma
Type : Miniature Sheet, Mint Condition
Colour : Multi Colour
Denomination : 500 Paise (8)
Stamps Printed : 0.5 million each
Miniature Sheet Printed : 0.1 million
Printing Process : Wet Offset
Printer : India Security Press, Nashik
About :
- On 26th April, 1942 Gandhiji wrote an essay on ‘Quit India’ in the ‘Harijan Patrika’. Thereafter, the notion of Quit India Movement was started on 14th July, 1942, when the Congress Working Committee approved a resolution which declared that ‘the immediate ending of British rule in India is an urgent necessity both for the sake of India and for the success of the cause of the United Nations’. On 8th August, 1942, Mahatma Gandhi launched the Quit India Resolution for freedom from British rule during the All India Congress Committee (AICC) meeting at Gowlia Tank Maidan, Mumbai (now known as August Kranti Maidan).
- The movement was accompanied by a mass protest on non-violent lines, in which Gandhi called for “an orderly British withdrawal from India”. In a stirring speech Gandhiji told the people, “There is a mantra, a short one, that I give you. You imprint it on your heart and let every breath of yours give an expression to it. The mantra is do or die. We shall either be free or die in the attempt….Every one of you from this moment consider himself a free man or women and even act as if you are free and no longer under the heel of this imperialism”. These words created an “electric atmosphere” in the country.
- The failure of the Cripps Mission was another event which triggered off the Quit India Movement.
- Following were the salient features of the Quit India Resolution launched by Gandhiji:
- 1. Hartals (strikes) in all cities and villages throughout the country.
- 2. All countrymen were promoted to self-made their salt as it is a prime necessity of our life.
- 3. Students above 16 may leave their college and universities and conduct a non-violence struggle for India’s freedom.
- 4. Every man or women in the country carry on badge bearing the motto do or die.
- In the early hours of 9th August, 1942 all the top leaders, including Gandhiji, Jawaharlal Nehru and Maulana Azad, were arrested, and the Congress was declared an unlawful organization. Despite his failing health and the recent demise of his wife, Gandhiji who was in prison, took on a 21 day fast. The British released Gandhi due to his ill health, but Gandhi continued his opposition and asked for the release of the Congress leaders who were in prison. Gandhiji’s last minute exhortation “Do or Die” sank deep in the minds of the people and they were ready to make the supreme sacrifice to defy the government.
- A wave of anger swept the country. The protest began in the form of the innumerable strikes, meetings and processions in the major cities like Bombay, Calcutta, Delhi, Patna and Ahmedabad. And then, the ruthless repressive measures taken by the police and the army, who made the railways, post offices and other government properties their major targets. By the end of 1942, more than 60,000 people were arrested and, about 10,000 were killed. It, however, spread to the rural areas, and went underground in the urban areas.
- The British were prepared for this massive uprising. The British acted quickly and arrested thousands of people. Most of the leaders arrested had to spend the next three years in jail, until World War II ended. Apart from filling up jails with rebellious leaders, the British also went ahead and abolished civil rights, freedom of speech and freedom of press.
- The main centers of the Quit India movement were Satara of Maharashtra, Tamluk, Contai of Midnapore, Balurghat of West Dinajpur, Balia, Azamgarh of U.P., Naogaon of Assam. Among the notable leaders were Srinath Lal, Nana Patil of Satara, Chaitu Pandey of Balia, Matangini Hazra, Sushil Dhara of Tamluk, Punjab’s Fukonani, Assam’s Kanaklata Barua. At Midnapore, Bengal, Quit India Movement took form of a mass uprising. The peasant movement organised by Birendranath Shasmal (‘Desh Pran’) enable the rapid spread of the Quit India Movement. It had deep impacts at Dinajpur, Balurghat, Midnapore, Contai, Tamluk, Patashpur, Bhagwanpur, Sutahata, Nandigram, Mahishadal, Birbhum, 24 Parganas etc. On 29th September 1942, under the leadership of 72 years old Matangini Hazra and Ramchandra Bera a mass of 20,000 seized the court and police station. When police opened fire on this procession many along with Matangini Hazra died. After Matangini the leadership was taken by Ajay Mukherjee, Sushil Dhara, and Satish Samanta and they captured Lalbari. On 17th December 1942 A.D. Ajoy Mukherjee formed the “Tamluk Provisional National Government”. They formed an armed force called ‘Bidyut Bahaini’ and women organization ‘Bhagini Sena’.
- The significance of Quit India Movement is that the British realized that they would not be able to govern India successfully in the long run and began to think of ways they could exit the country in a peaceful and dignified manner. The Quit India Movement proved the power of the masses.
- Text : Based on the material available.







[…] the Prime Minister (it was the contemporary form of address) of Madhya Pradesh. He took part in Quit India movement, and relinquished his post by the end of 1939. Again in 1945, he held the reigns of Madhya […]
[…] C. Kesavan briefly worked as a school teacher. His political career began in 1932 as the undisputed leader of Abstention Movement (Nivarthana Agitation). As a leader of this Movement, which later shaped the struggle for Independence in this part of the country, he entered mainstream politics through the State Congress. He invited the severe wrath of the rulers while serving as the general secretary of All Travancore Joint Political Congress. He was arrested at Alleppey on June 6, 1935, tried for sedition, sentenced to imprisonment and fined and confined to Central Prison, Thiruvananthapuram. He made an epoch-making speech in Kozhenchery in 1935 which was a turning point in his career and a milestone in shaping the destiny of modern Kerala. C. Kesavan was arrested and imprisoned in Central Jail, Poojappura, Trivandrum. Later released, he was given a rousing reception at Kidangaparambu, Alappuzha. With the establishment of Travancore State Congress in 1938, the stormy political life of C. Kesavan had begun. Later, he courted arrest frequently and became a regular visitor to Poojappura Central Prison in Trivandrum. He had to again undergo imprisonment from August 29, 1942 for one year for taking part in the Quit India Movement. […]
[…] ‘Quit India’ Movement of 1942 was a watershed in India’s struggle for freedom. It was this movement that […]
[…] which took place in Ballia in Uttar Pradesh is one among the most inspiring chapters of the Quit India Movement of […]
[…] in class X, he was arrested for picketing at the main gate of his school at Buxar in support of 1942 Quit India Movement. He was affiliated with the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh from 1944 onwards, and was jailed after the […]
[…] the Praja Mandal movement and was drawn to the freedom struggle in his student days. During the Quit India Movement he was imprisoned for 1½ years. He became the Minister of Civil Supplies, the Public Works […]
[…] also seen in action in the Russian theatre of war. In 1942, he became an active participant of the Quit India movement. He was imprisoned in 1942 and was released only in 1946. Later on, accompanied by his […]
[…] the Quit India Movement, Gandhiji gave the clarion call ‘Do or die’. A great movement to oust the British was […]
[…] The freedom movement had inspired Shyam Narayan Singh at a young age, and he actively participated in various struggles that Bihar witnessed. He was targeted by the authorities, and starting with a nine-month prison term in 1937, he came into confrontation with the foreign rulers on many occasions. There was a shoot at sight order on him during the 1942 agitation. […]
[…] in social upliftment of the weak and the poor. While doing his graduation, he left college to join Quit India Movement on the call of Mahatma Gandhi. As an ardent activist of freedom movement, he had to undergo […]
[…] Movement such as Salt Satyagraha (1930), Civil Disobedience (1932), Individual Satyagraha and Quit India Movement (1942). He authored many books, the most noteworthy being, ‘History of the Indian National […]
[…] struggle. He also undertook a 400-mile long ‘padyatra’. He actively participated in the ‘Quit India’ Movement in 1942 and was imprisoned by the colonial […]